What are the Signs of Diabetes (and How to Prevent Becoming Diabetic)

What are the signs of diabetes? Unfortunately, a staggering amount of patients at Hillandale Primary Care come to us with concerns about diabetes. What’s even more unfortunate is that 34.2 million Americans, or 1 in 10, have diabetes. Meanwhile, one and three adults in the United States have pre-diabetes.
Unfortunately, diabetes is here to stay. Some people who have diabetes can control it without medication and return to glucose levels that are in non-diabetes range, otherwise known as complete remission. This applies to type 2 diabetes, although there is no cure it is possible to reverse it.
Meanwhile, type 1 diabetes is treatable with insulin injections. A treatment plan can help reduce symptoms, but there is no cure. Unlike Type 2 Diabetes, Type 1 diabetes cannot be reversed.
However, you might be wondering if you have diabetes in the first place. Let’s talk about what you might experience if you have diabetes or even pre-diabetes.
What Are The Signs Of Diabetes?
Both type one and type two diabetes come with similar symptoms. If you are diabetic, you will Likely experience many if not all of the following symptoms:
- Frequent urination at night
- You’re very thirsty and drink a lot of fluids
- You lose weight even though you aren’t trying
- You have blurry vision
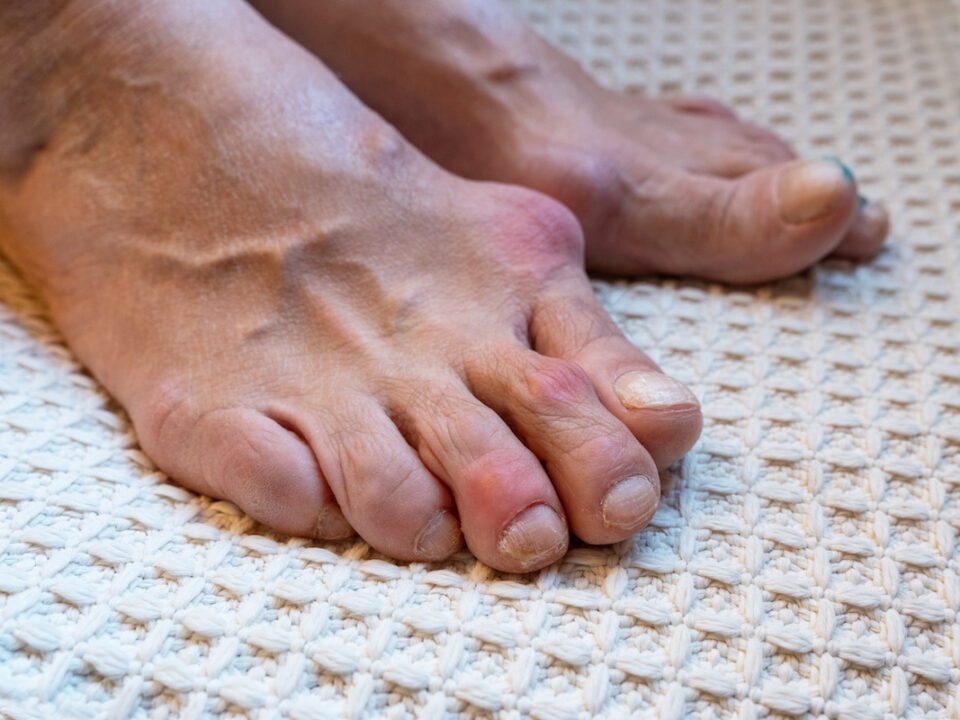
- You have numb and tingling feet or hands
- You are fatigued often
- You have sores that heal more slowly than other people
- You have a lot of infections
- Type 1 diabetics may also experience nausea and vomiting
If you are experiencing these symptoms without seeking treatment, it’s time to schedule an appointment with Hillandale Primary Care. One of the first steps is to check your blood sugar levels to make sure they are within an appropriate range. If there are concerns, you will be provided with insight on how to manage your blood sugar, and you’ll return for another checkup appointment at a later date. Your blood sugar levels will be tested again to see where you stand.
What is Pre-Diabetes?
As you can see, there are different variations of diabetes that you can encounter. One of those is pre-diabetes. But what is pre-diabetes?
If you have pre-diabetes, it means that you have a higher than normal blood sugar level. However, it is not high enough to be considered type 2 diabetes.
The good news is that you will not inevitably progress to type 2 diabetes if you’re pre-diabetic. However, adults and children are likely to develop type 2 diabetes through lifestyle interventions and changes.
If you have pre-diabetes, this is not a diagnosis to take lightly. The problem is that damage from diabetes may already be happening to your heart, blood vessels, and kidneys.
However, you might come to the clinic and discover that you have type 2 diabetes. Let’s take a look at what type 2 diabetes is and what this means.
What is Type 2 Diabetes?
Type 2 diabetes means that there is an impairment in the way that your body uses and regulates sugar, otherwise known as glucose. This is a chronic and long-term condition that means that there’s too much sugar circulating in your bloodstream. These high blood sugar levels can lead to an array of health conditions and symptoms, including the circulatory, nervous, and immune systems.
Meanwhile, with type 2 diabetes, your pancreas is not producing enough insulin, which is a hormone that helps regulate sugar in your cells.
Keep in mind that type 2 diabetes is commonly onset in adulthood, but with an increase in childhood obesity, kids can have type 2 as well.
What is Type 1 Diabetes?
Just like Type 2 Diabetes, Type 1 diabetes also means that your pancreas does not make enough insulin. Type 1 diabetes is also most commonly diagnosed in children, teens, and young adults, although it can have an onset at any age.
Meanwhile, type 2 diabetes is also a lot less common and type two. In fact, only 5 to 10% of people with diabetes have type 1. There is currently no known prevention to type 1 diabetes, but it can still be managed.
Who is Most Susceptible to Diabetes?
Now that you understand all about prediabetes, type one, and type two, you might be wondering who is the most susceptible to developing diabetes. Here is some insight on this question:
- You are 45 years of age or older, which is the group that is most likely to develop type 2
- You have a family history of diabetes
- You are overweight or obese
- Diabetes is the most common in Black, Hispanic/Latino, American Indian, American Asian, and Pacific Islander groups
- You are physically active less than 3 times a week
- You have non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
- You had gestational diabetes while pregnant or you had a baby that weighed more than 9 pounds
If you met some or all of the points on this list, it does not mean that you will automatically become diabetic. However, it does increase the likelihood that you will develop diabetes at some point in your life. Therefore, it is very important to take proper precautions to prevent the onset of diabetes.

How to Prevent or Reverse Diabetes
Diabetes prevention and reversal applies to those who do not have diabetes, are pre-diabetic, or were diagnosed with type 2 diabetes. In terms of diabetes prevention, these are some of the guidelines that you can follow.
Cut out Sugary Drinks
A healthy diet is a major part of preventing or reversing diabetes. There are several aspects where you will want to reduce or remove entirely from your daily menu.
For example, sugary snacks and drinks are associated with an increased risk of developing diabetes. In fact, women who drink one or more sugar-sweetened beverages per day have an 83% higher risk of developing type 2 diabetes. This is in comparison to women who only drink one or fewer sugar-sweetened beverage per month.
Meanwhile, for every additional 12-ounce serving of sugary beverages per day, the risk of developing diabetes rises by 25%.
If you are accustomed to drinking sugary drinks, whether it’s a coke or diet coke, it can take some work to change your habits. Replacing your sugar-filled drinks with water or black coffee can be an excellent way to decrease sugar in your diet. It’s very easy to disregard calories in sugar and drinks, but it’s critical when it comes to preventing or reversing diabetes.
Choose Whole Grains Over Refined and Highly Processed Carbohydrates
If you have a daily sandwich with white bread, there is some swapping to do to make your meal healthier. Refined and processed carbohydrates are on the high glycemic index and include foods such as sodas, candy bars, bagels, waffles and pancakes, white rice, breakfast cereals, pizza, ketchup, BBQ sauce, and much more.
You’ll want to stick with whole grains and carbohydrates that are lower on the high glycemic index. For example, vegetables have carbs, but they are not the same type of carbohydrates that you will find in a McDonald’s combo meal.
The idea is to stick to carbs that are as unprocessed as possible. This can include beans that you cook in a pressure cooker. Fruits, vegetables, and brown rice also make the list.
The best way to avoid refined carbohydrates is by carefully reading food labels and avoiding sugar as much as you can. Cooking at home will allow you to know exactly what is in the food you are eating. There are plenty of diabetic-friendly recipes that you can find online. You can also find diabetic cookbooks for free at the library. Diabetics are not destined to live with bland diets!
Get Plenty of Exercise
We are all busy and exercise may be low on your priority list. Those with busy lifestyles and kids can find it especially hard to exercise as needed.
However, it’s incredibly important that exercise becomes a priority for your lifestyle. How much exercise do you need to prevent or reverse diabetes?
You’ll need at least 150 minutes of aerobic activity or 75 minutes of vigorous exercise per week. You can also combine aerobic activity with vigorous exercise.
Don’t forget that strength training is also an important part of physical fitness. You will need to do strength training for all major muscle groups two times per week.
If you are a beginner at exercise, you will want to ease into a program under the advice of a doctor. Know that walking is also a great exercise, as it’s low impact and many people are able to do it. There are also seated exercises that you can do with and without weights.
Manage Your Diabetes with Hillendale
If you are concerned that you have diabetes or you are looking for help with management or prevention, Hillendale is here to help. Please contact our office to schedule an appointment, where we can give you personalized advice on how to approach your situation in the best way for you.